How to Know Symptoms, Types and Causes Ovarian Cancer? Women Must Read. Ovarian cancer is a silent killer, which means that symptoms often do not appear at an early stage of its development. Symptoms of ovarian cancer are often first discovered in the next stage at which time it is already difficult to cure ovarian cancer.

Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
Symptoms of ovarian cancer the most common is distended or bloated in the stomach, feelings of anxiety or pain in the pelvic area, stomach pain, eating disorders, or a feeling of fullness in the abdomen, and urinary symptoms such as frequent urination or bladder that is always feeling full.
Other symptoms of ovarian cancer include constipation, pain during intercourse, menstrual cycle changes or bleeding between two menstrual periods, back pain, and weakness.
If frequent constipation, but in a short time, and constipation you heal yourself or cured with medication, then perhaps it's not ovarian cancer. The possibility of ovarian cancer if constipation occurs is longer than usual and did not recover after taking the usual medicines.
If you feel the bloating / distended every time after eating certain foods and then lost, most likely it is not associated with ovarian cancer.
If constipation, abdominal or pelvic pain has lasted more than a week, you should immediately consult a doctor.
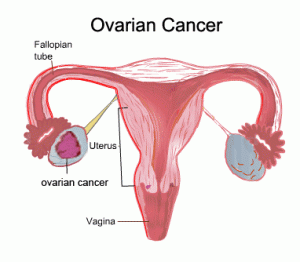
Type of Ovarian Cancer
Identified more than 30 types and subtypes of ovarian cancer in women. But most experts categorize them in one of three categories:
Epithelial Tumors. Derived from the epithelial cells lining the surface or ovaries. This type is most common, approximately 90% of all ovarian cancers.
Germ Cell Tumors. Derived from ovarian cells that eventually become eggs. It usually occurs in adolescents and young adults. Tumors can often be cured is filled up about 3% of all cases of ovarian cancer in developing countries.
Sex-cord Stromal Tumors. Fill about 5% of all ovarian cancers. Derived from cells that turn into the connective tissue in the ovary.
Germ Cell Tumors. Derived from ovarian cells that eventually become eggs. It usually occurs in adolescents and young adults. Tumors can often be cured is filled up about 3% of all cases of ovarian cancer in developing countries.
Sex-cord Stromal Tumors. Fill about 5% of all ovarian cancers. Derived from cells that turn into the connective tissue in the ovary.
Causes of Ovarian Cancer
The exact cause of ovarian cancer is unknown. The researchers analyzed several factors that can increase a woman's risk for ovarian cancer, although experts have not found a reason these risk factors can increase the risk of ovarian cancer. These risk factors are:
Aged over 50 years. Women aged over 50 years are more at risk than women aged below it. Most ovarian cancers develop after menopause. Experts speculate that changes in hormones are a trigger, plus the old woman has undergone many ovulatory cycles throughout their lives. Indeed, the case of women under the age of 40 years who develop ovarian cancer is rare, but remember that ovarian cancer knows no age limit.
Obesity or being overweight. Women who have a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 30 or more, then more be at risk. There is a theory that fat cells contain estrogen more than other cells, although it is not known how the increase in estrogen plays a role in this regard.
Has never been pregnant, or become pregnant in first at the elderly. Women who have never given birth have a higher risk of ever giving birth. And the risk will fall pregnant each time.
Not breastfeeding. Women who do not breastfeed are more at risk than women who are breastfeeding.
The use of fertility drugs. Using a fertility drug Clomid in a period of more than one year would increase the risk of ovarian cancer.
Estrogen hormone replacement therapy. Some studies suggest that women who undergo estrogen replacement therapy after menopause have an increased risk of ovarian cancer, especially if using estrogen alone (without progesterone) for 5 years or more.
Genetic. No family ever developing ovarian cancer, breast or colon cancer will increase the risk of ovarian cancer. The study says that 10% of ovarian cancers have a tendency inherited from family. The risk will be increased if more families were affected by ovarian cancer.
Gene mutations. There are families affected by cancer of mutations (changes) gene, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, also will increase the risk of ovarian cancer and breast cancer. A gene mutation that increases the risk of colon cancer, may also increase the risk of ovarian cancer.
Breast cancer. If you have breast cancer, then it is likely to develop ovarian cancer is greater.
Diets high in meat. Research shows that women with a low-fat diet or a diet high in vegetables have an increased risk of ovarian cancer are lower than those whose diets are high in fat (especially animal fat) and low in vegetables.
Smoking and alcohol. Both of these habits will increase the risk of epithelial ovarian tumors.
Reveal the risk factors of ovarian cancer is not as easy as heart disease or breast cancer, because the disease has not long been investigated intensively.
Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer
By regularly check the pelvis, the presence of tumors or enlargement of the ovaries will be known, although small tumors can not be detected by these tests. Imaging tests such as transvaginal ultrasound can detect any abnormalities.
When small tumors may not be detected by ultrasound, the doctor may also perform other imaging techniques such as CT (computed tomography), MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) or PET (positron emission tomography) scans. Everything will provide images of the pelvis and reproductive organs.
Your doctor may also do a blood test, known as CA-125, which shows the levels of the marker protein, which increase may indicate ovarian cancer. But this test is not necessarily accurate because there are several other conditions that could also increase the levels of CA-125. And also a woman who had ovarian cancer, but levels of CA-125 is still normal.
Ovarian cancer can only be diagnosed with certainty by looking pieces / ovarian tumor samples with a microscope. To obtain ovarian tissue that is abnormal, the doctor will perform a laparoscopy to look into the abdomen and pelvis with a kind of long tube that is inserted into the body through a small incision in the abdomen or pelvis. Or by performing open surgery.
Treatment of Ovarian Cancer
Treatment for ovarian cancer consists of surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Sometimes doctors apply two or three of these methods for treating ovarian cancer.
Surgery may be performed to determine the stage of the cancer and remove the tumor as much as possible. The number of operations will depend on the stage of the cancer and your health.
If you are in the fertile age, and early-stage ovarian cancer, doctors may be able to treat it without lifting the uterus or ovaries.
For epithelial ovarian cancer, chemotherapy through an IV usually consists of a combination of drugs given in six cycles, each cycle is about 3-4 weeks. Another option is chemotherapy intraperitoneal (IP), given through a thin hose is placed in the stomach.
Radiation therapy is used to treat ovarian cancer is called external beam radiation (external beam radiation). An engine (from outside the body) emits radiation to the cancerous area. Interval irradiation will depend on the type and stage of ovarian cancer.
Things to Remember
An American Cancer Society statistics show that about 3 out of 4 women with ovarian cancer survive only about 1 year of diagnosis. Nearly half (46%) of women with ovarian cancer are still alive at least until 5 years after diagnosis.
Several points regarding ovarian cancer you need to remember and anticipation, namely:
Learn the risk factors of ovarian cancer, and find out whether you are in the position of one of these risk factors.
Learn your family's medical history. If you have a family history of breast cancer, ovarian cancer or colon cancer, consult your doctor immediately, you may need a genetic test.
Know the symptoms associated with ovarian cancer. If you have any symptoms for more than a week, consult a physician.
Rutinlah went to the doctor for a pelvic exam. It is very important for menopausal women or who have risk factors for ovarian cancer.
Keep your weight (BMI less than 25). Use the BMI calculator Medkes gauge.
Eat a healthy diet, and plenty of vegetables. Do not consume saturated fat.
Thank you and may be helpful
source : medkes.com

